During its one-year funding period, this CISESS Seed Grant project expanded the work of the student-oriented CISESS Remote Sensing Laboratory by building equipment for post-launch radiometric validation of satellite senor using in situ measurements of reflective solar band. ESSIC/CISESS Scientist Xi Shao, along with Sirish Uprety, Tung-Chang Liu, and Xin Jing, developed a Robotic Hyperspectral Ground Bi-directional Reflectance Distribution Function (RHG-BRDF) measurement system.

Once built, they worked with three undergraduate students to perform field hyperspectral measurements of different ground targets. The student also developed python modules for converting measurements to hyperspectral reflectance, data visualization and analysis.
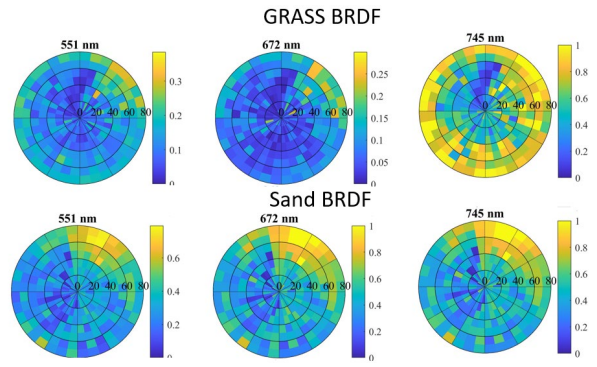
The Remote Sensing Laboratory activities fostered a broader scope of collaboration and engagement between the UMD/CISESS team and the NOAA sensor calibration team. They also contributed to the development of a portable Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS) at the NOAA/STAR National Calibration Center (NCC) laboratory for ground-based atmospheric trace gas measurements.






