Exploring Super Resolution Satellite Images with Artificial Intelligence
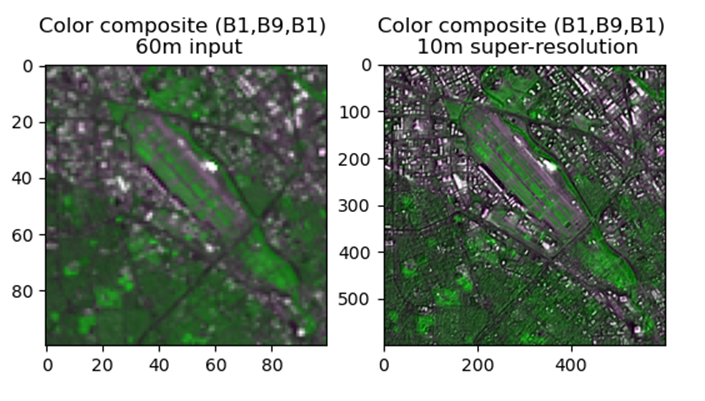
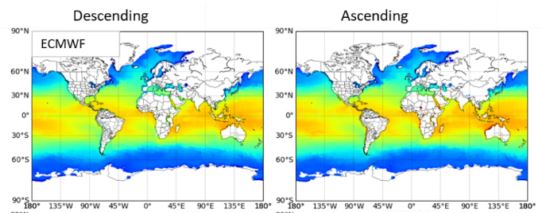
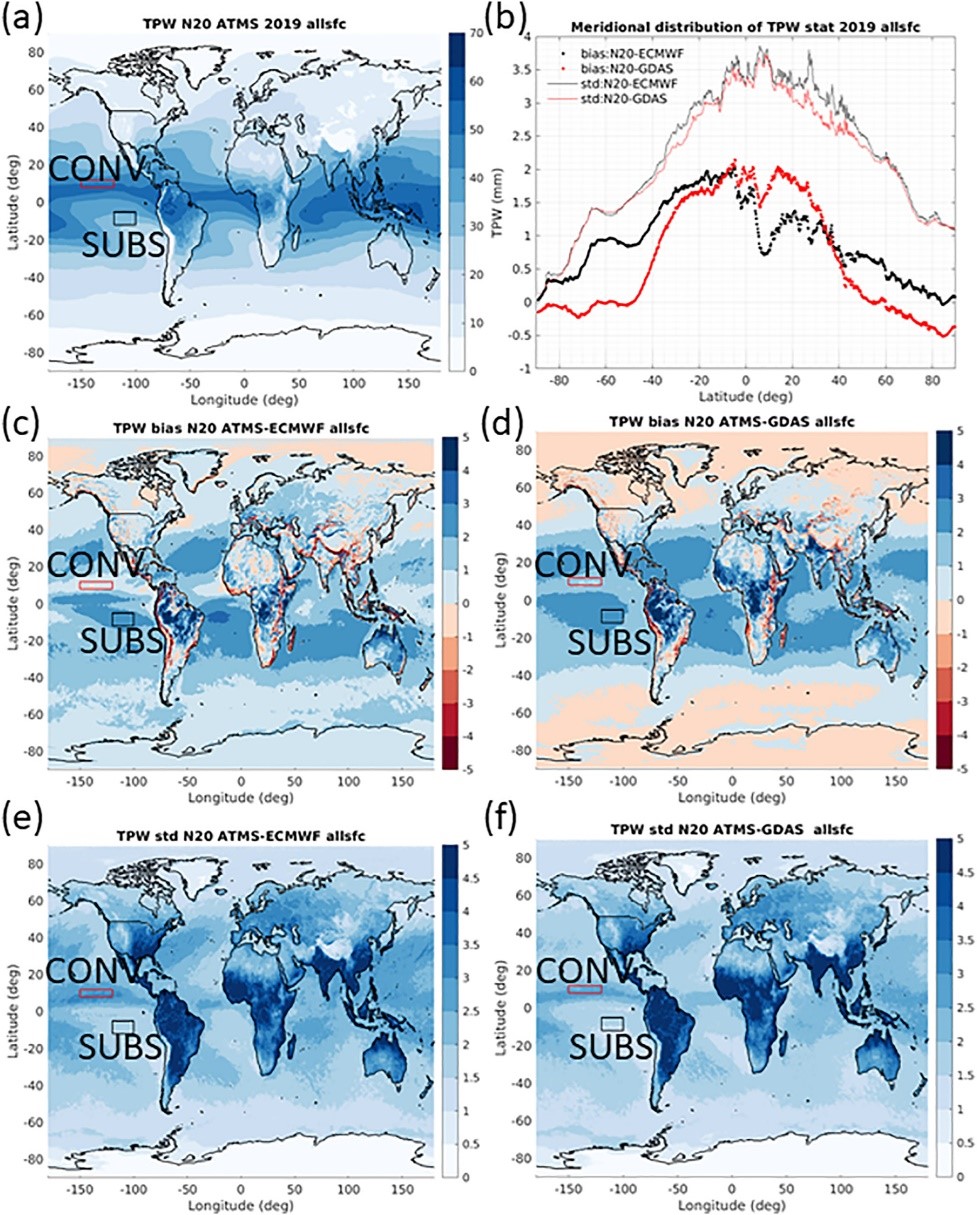
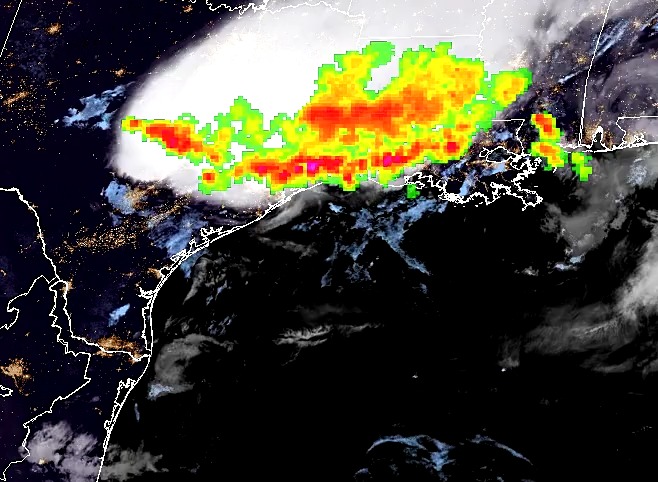
NOAA Center for Satellite Applications and Research (STAR) scientists are exploring new capabilities of enhancing satellite images with artificial intelligence (AI) so that moderate resolution images could be enhanced to include more detailed features with high resolution.