
ESSIC Scientists Attend 2021 Mid-Atlantic ChaserCon
ESSIC/CISESS lightning team scientists Joseph Patton and Daile Zhang attended the 2021 Mid-Atlantic ChaserCon, held at the Science Museum of Virginia in Richmond, VA on November 6th.

ESSIC/CISESS lightning team scientists Joseph Patton and Daile Zhang attended the 2021 Mid-Atlantic ChaserCon, held at the Science Museum of Virginia in Richmond, VA on November 6th.
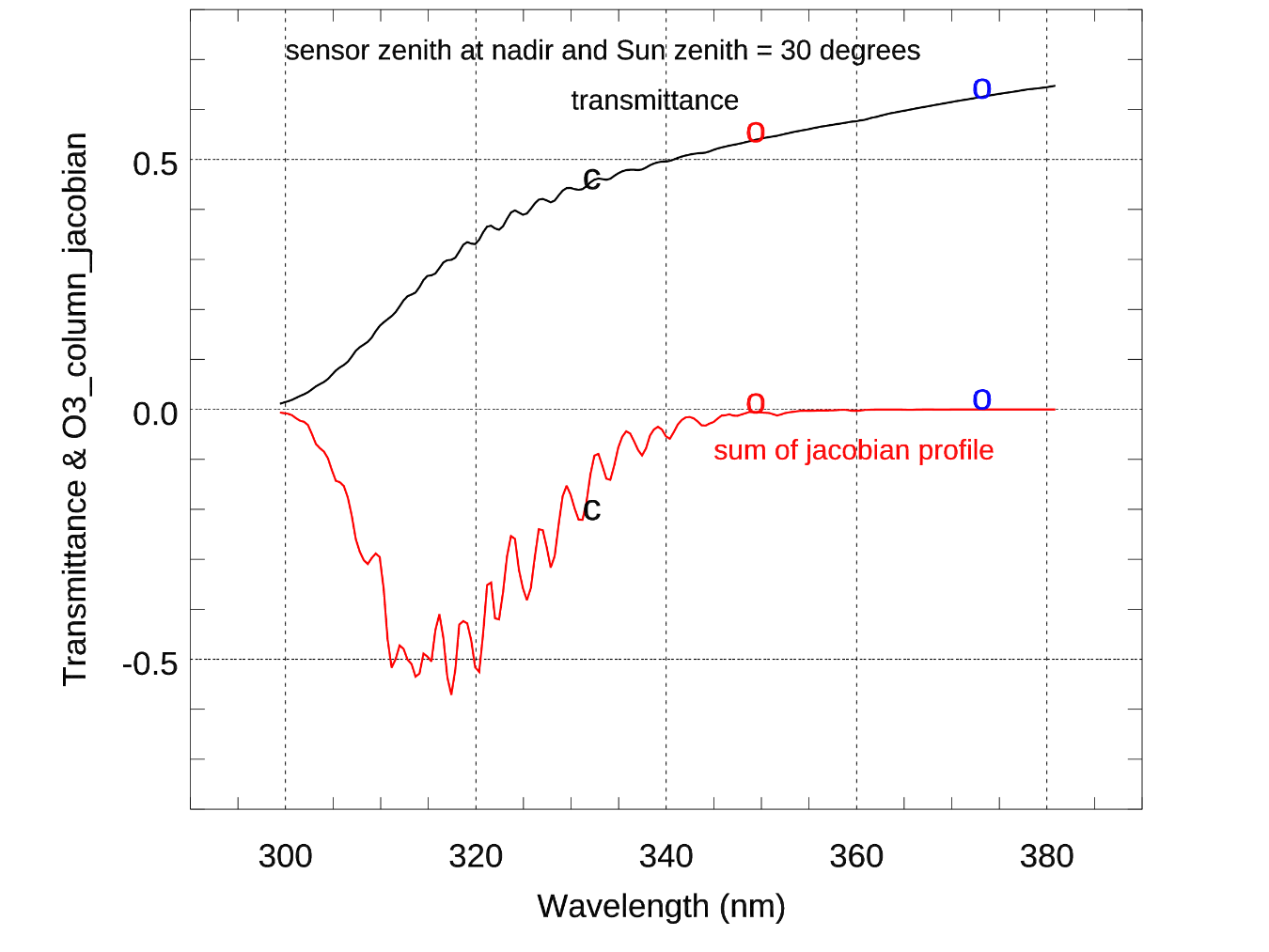
ESSIC/CISESS scientists Christopher Grassotti and Xingming Liang are co-authors in a recently published study that documents the first ultraviolet radiance assimilation for atmospheric ozone in the troposphere and stratosphere. The paper, titled “Experimental OMPS Radiance Assimilation through One-Dimensional Variational Analysis for Total Column Ozone in the Atmosphere”, was published in Remote Sensing and includes co-authors from the NOAA/NESDIS Center for Satellite Applications and Research.

This week, ESSIC/CISESS Scientists Joseph Patton and Guangyang Fang and Summer Intern Terrence Pierce visited one of our lightning detection stations on the campus of Howard University-Beltsville. The GPS antenna for the station had been giving them trouble, so they installed new connectors for the cable that connects the GPS antenna to the lightning detection computer, and that seems to have resolved the problem.
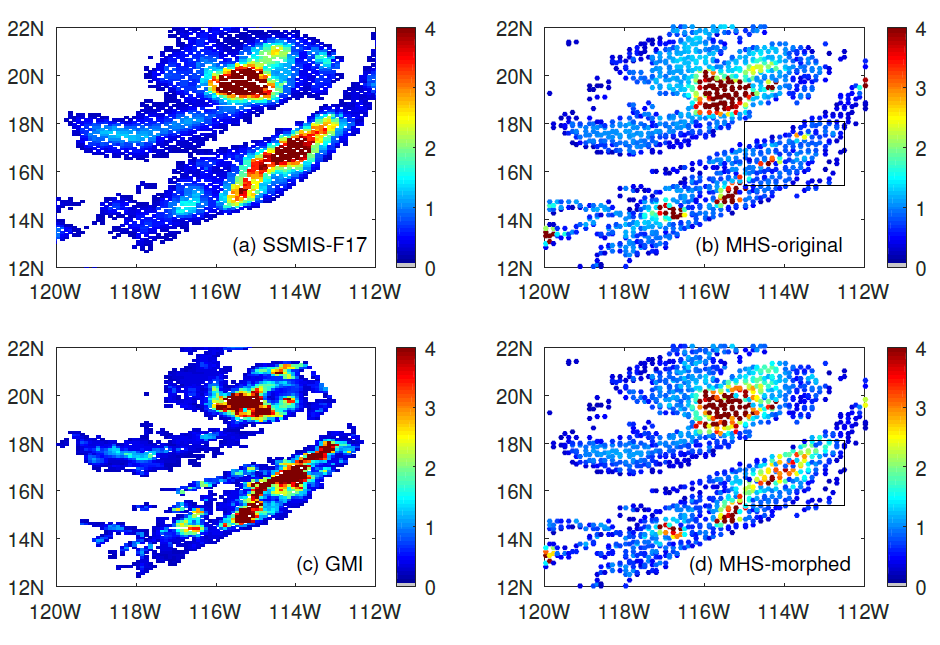
ESSIC/CISESS Scientists Yalei You, John Xun Yang, and Jun Dong have a new article on using “morphing” to improve rain data from cross-track scanning radiometers. The paper, titled “Improving Cross-track Scanning Radiometers’ Precipitation Retrieval over Ocean by Morphing”, is in press at the Journal of Hydrometeorology.

Congratulations to Xin-Zhong Liang, newly elected Fellow of the American Meteorological Society (AMS). This honor is an apt recognition of his vigorous multidisciplinary research efforts and notable achievements.

ESSIC/CISESS Scientists Xin Jing, Xi Shao, Tung-Chang Liu and Bin Zhang (STAR/SOCD) have a new article in the July 2021 issue of Atmosphere titled “Comparison of GRUAN RS92 and RS41 Radiosonde Temperature Biases”.
ESSIC/CISESS Assistant Research Scientist Junyu Qi and Visiting Research Scientist Xuesong Zhang are co-authors on a recent paper titled “Pronounced Increases in Future Soil Erosion and Sediment Deposition as Influenced by Freeze–Thaw Cycles in the Upper Mississippi River Basin”.

Several ESSIC/CISESS scientists including Malarvizhi Arulraj, Jifu Yin, Christopher Grassotti, Veljko Petkovic collaborated on a multi-author, two-part study led by Douglas Miller, Professor of Atmospheric Sciences at the University of North Carolina, Asheville.
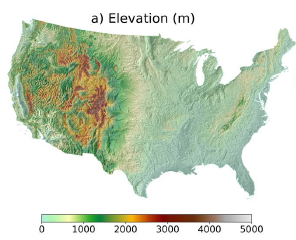
ESSIC Visiting Assistant Research Scientist Huan Wu has a new paper in Journal of Hydrometeorology titled “Assessment of Precipitation Error Propagation in Discharge Simulations over the Contiguous United States” alongside Naijun Zhou from UMD’s Department of Geographical Sciences.

ESSIC/CISESS Scientists Xi Shao, Sirish Uprety and Wen-hui Wang are contributors to a new book, Remote Sensing of Night-time Light, to be released on August 10th. Their chapter is on the assessment of straylight correction performance for the JPSS Visible/Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) day/night band using Dome-C and Greenland under lunar illumination. This book captures key methodological issues associated with pre-processing night-time light data, documents state of the art analysis methods, and explores a wide range of applications.